There is probably not a single person who has not heard of Bitcoin, cryptocurrencies, and blockchain technology. Cryptocurrency and blockchain are slowly making their way into people’s everyday lives. Some appliance stores and restaurants have begun accepting cryptocurrency instead of traditional money. Blockchain technology has found application in logistics and supply chain management. According to Verifiedmarketresearch, the market size of blockchain in logistics was valued at USD 3.3 Billion in 2020. It is projected to reach USD 1620 Billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 62.4% from 2021 to 2028.
In our article, you will find out what supply chain management is and the benefits of blockchain technology in supply chain management. We’ll also show real-world use cases of blockchain in logistics and challenges for blockchain implementation in supply chain management.
Key points
What is Supply Chain Management
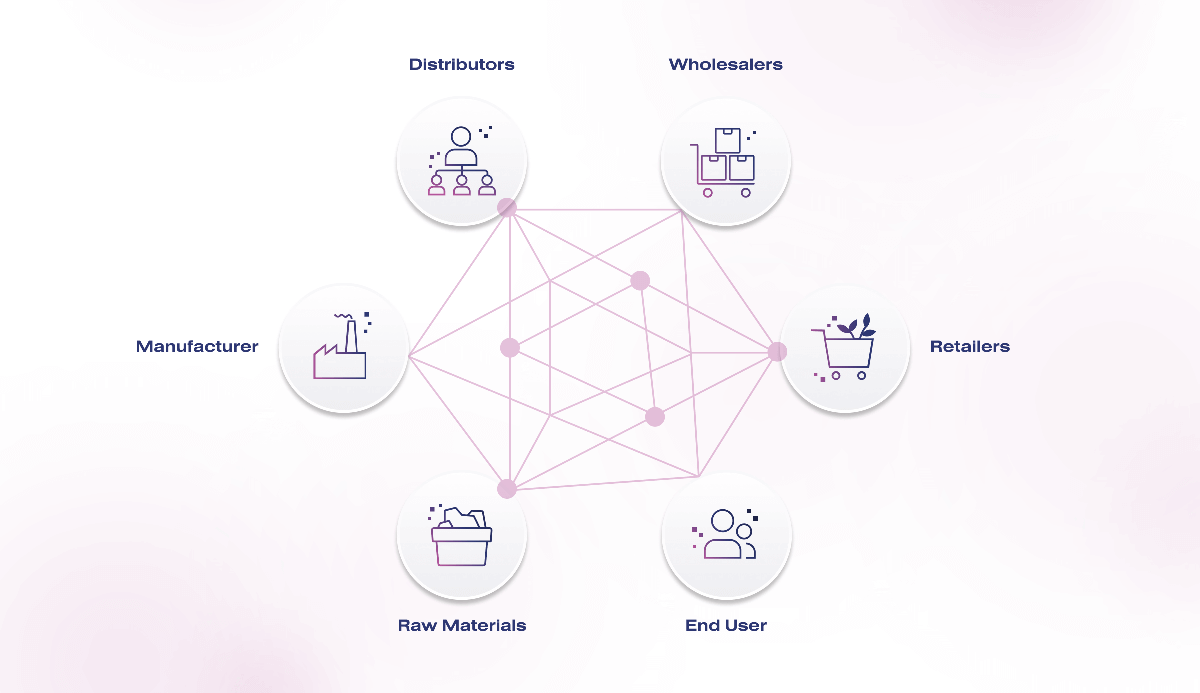
Supply chain is the set of organizations, people, technology, processes, information, and resources involved in moving a product or service from supplier to customer. Supply chain management means distributing materials, information, and funds from supplier to customer.
For a company, the two main aspects of a successful supply chain are:
- Reducing working capital requirements by reducing inventory (being profitable and being able to invest in research and upgrading production)
- Improving customer service through a well-managed supply chain
Introducing blockchain into logistics will ensure data security, protect the document repository from hacking, and eliminate the possibility of altering shipping information. Such a system can definitely reduce delivery delays and the likelihood of fraud, saving billions of dollars for everyone involved in the supply chain. According to the World Trade Organization, eliminating barriers in the international supply chain can increase global GDP by 5% and total shipments by 15%.
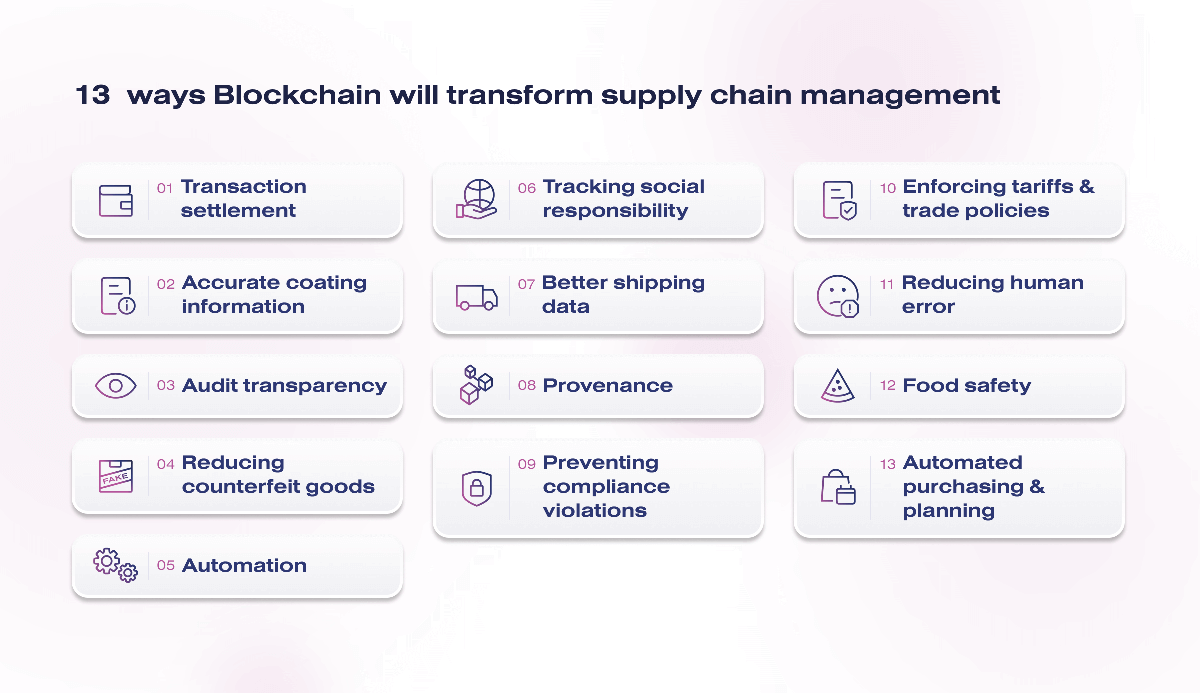
Benefits of blockchain technology in supply chain management
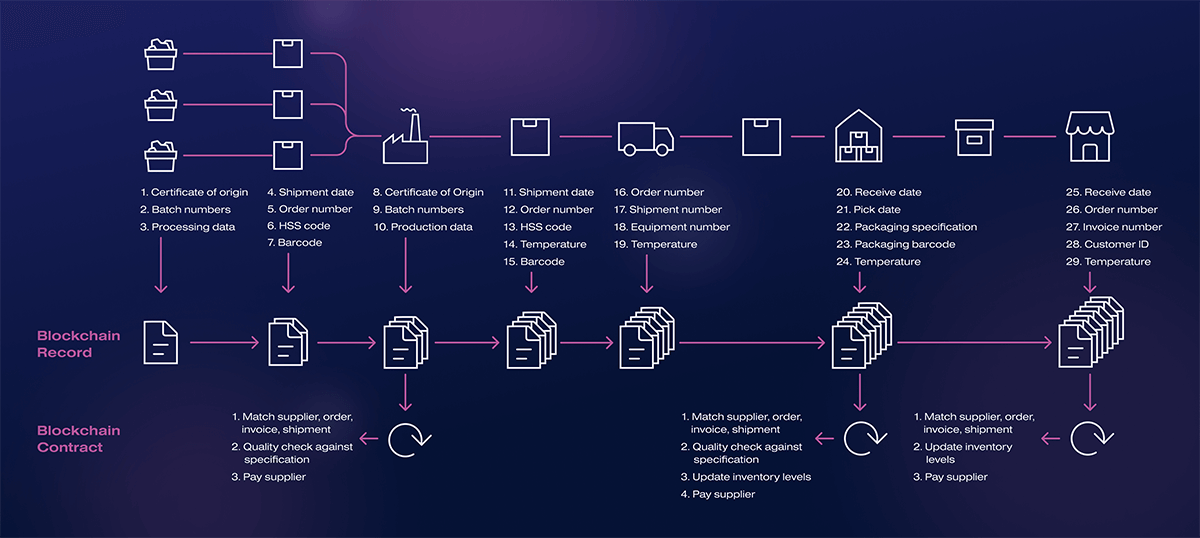
Transport logistics is part of the international shipping industry. The process of cargo delivery often has pitfalls.
The problem of finding cars and cargo for both sides is still relevant, despite the development of Internet technology. This is what intermediaries take advantage of. The presence of extra people chain increases the cost of transportation. Smuggling is flourishing on the market due to the owner’s inability to control the cargo on the way.
The interaction between officials, logisticians, and freight forwarders complicates the delivery process. The situation is aggravated by customs issues and paperwork associated with permits and cargo declarations. These problems can be solved by introducing blockchain, which can change the transportation workflow.
The main benefits of blockchain technology in logistics and supply chain management:
- Allows for cheaper logistics
- Eliminates the possibility of data tampering – a document entered once (bill of lading, receipt, certificate of compliance, etc.) remains in the system in its original form forever
- Eliminates unnecessary intermediaries
- Prevents mislabeling of illegal goods and other fraud attempts
- Allows for a great reduction of time for document turnover
- Quickly finds the link of transportation where an error was made
- Reduces business costs due to losses
These are benefits blockchain can bring to supply chain management. But how does blockchain work?
A timestamp (hash sum) is added to each block (it can be simply represented as a unique fingerprint). These blocks are stacked into chains in a strictly defined order. If someone tries to rearrange the sequence of the blocks, the system will reject the chain because the structure and the hash sum do not match. Blockchain uses several methods of protection: Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS). They are needed to prevent anyone from changing the timestamp and recalculating the hash sum that would be correct from the system’s point of view.
Logistics Industry Use Cases
- Retailer Walmart was one of the first to believe in the promise of blockchain technology. It tested IBM’s new technology on shipments of pork in China and mangoes in the United States. The company believes that implementing blockchain will ensure the safety of food shipments and improve inventory management, which Walmart believes is especially important after the outbreak of intestinal infection in 2006. At the time, in an era of paperwork, it took the company about two weeks to find the source of the infection. With blockchain, it would be possible to retrieve information about any shipment in the database in a matter of seconds.
- Wells Fargo, Brighann Cotton, and Commonwealth Bank of Australia conducted a joint logistics experiment in 2016. The experiment shipped 88 bales of cotton worth $35,000 from the U.S. to China. The goods were unloaded in the port of Qingdao after a journey of 11,000 kilometers. As a result, the companies got confirmation that the combination of blockchain technology and smart contracts brings real benefits to the business.
- Trucking company FedEx has partnered with Blockchain in Transportation Alliance (BiTA). The company was working on a pilot project for data storage. It determines what data is needed for a permanent registry, which will then be used to resolve disputes between the company’s customers. Blockchain-based platforms will help customers track parcels more efficiently, not just when FedEx handles them but at every stage of the delivery process.
- EverLadger uses blockchain to confirm the source of origin in the diamond trade in the supply chain.
- Princes uses blockchain to create end-to-end transparency in the tuna chain.
- The Port of Rotterdam has been testing blockchain logistics technology since 2016. It helps to develop transparency in the industry. The project has been supported by more than 15 private and public sector companies based in the Netherlands with the help of the Ministry of Economic Affairs and Climate Policy.
- The Port of Antwerp announced in June 2017 the launch of a pilot blockchain project to optimize logistics processes. The testing was done in collaboration with blockchain startup T-Mining. They believe that blockchain technology has the potential to increase the transparency of data exchange and speed up the interaction between logistics process participants and port customers. This, in turn, will minimize the likelihood of any data manipulation. By the way, CMA CGM will secure all import containers in the Port of Antwerp with T-Mining’s blockchain-enabled Secure Container Release (SCR) software solution.
Challenges and limitations of implementing blockchain in supply chain management
Despite the wonderful benefits of blockchain technology, there are also shortcomings. Challenges (they are limitations) that need to be addressed when implementing blockchain in logistics and supply chain management:
- Lack of standards. Unlike universal product codes and data interchange, blockchain technology is not standardized.
- Complex supply chains. Multi-ingredient supply chains have many pitfalls that must be considered.
- Time and cost. Initial costs of setting up and maintaining a blockchain are expected, while the time required for this is a pain point for most supply chains.
- Speed and scalability. Scaling blockchain is a huge pitfall because the computing power required for the transaction is enormous.
- Interoperability. End-to-end internal and external integration with existing systems is needed to reach excellent results in value provided by the blockchain.
- Government buy-in. Blockchain disrupts many processes and systems that governments are based on.
Therefore, it’s crucial to introduce blockchain technology in any niche with the high-skilled transportation and logistics software team. You can see our case studies on our website right now!
What is the future of blockchain in logistics and supply chain management?
The future of blockchain depends on many factors. The final stage in blockchain’s proliferation in supply chain management involves scaling the solution and realizing its benefits. An analogy is Facebook: the value of a community grows as more people connect to it.
Blockchain is not yet a mature technology and is not being used on a large scale. As a technology, blockchain appeared in 2008, but it was only mentioned separately from cryptocurrency in 2017. Introducing the technology into supply chain management takes a lot of work: companies must test it and then agree on rules with other participants. It can take several years to create such ecosystems.
For starters, all business participants using blockchain should agree on what rules of the game to apply. Blockchain solutions are spreading in the market, and market participants are consolidating under leading systems. We mean, for example, the R3 consortium in finance, MOBI in automotive, and Hyperledger in logistics. In such a way, it is easier and more convenient to get ideas for blockchain platforms, test different management models and refine business processes using the technology.
We also recommend you read another article about blockchain technology’s impact on e-commerce.
Conclusion
The general public only took Bitcoin and blockchain seriously a couple of years ago. As more information about the technology spreads, companies’ interest better transforms into investments. According to Infiniti Research Limited, the global blockchain technology market is expected to grow by $2230.89 mn from 2023 to 2027, accelerating at a CAGR of 39.78%. We are confident that introducing blockchain in logistics will greatly facilitate mass blockchain adoption.